Origin of the Pescatarian Diet | How Does the Pescatarian Diet Work? | Benefits of a Pescatarian Diet? | Environmental Impact of the Pescatarian Diet? | Pescatarian Diet Lead to Weight Loss? | What Do the Experts Say? | Bottom Line
Dieting for most people is usually a way to either lose weight or avoid gaining weight. For others, though, a chosen diet is about living a healthier life or aligning one’s lifestyle choices with a set of core beliefs. A great example of a diet like this is the pescatarian diet, a unique and increasingly popular dietary pattern that offers a fusion of plant-based foods and seafood. The pescatarian lifestyle, characterized by its emphasis on sustainability and overall health, may appeal to people with certain beliefs, but the diet itself has merit as a way to lose weight as well.
Origin of the Pescatarian Diet
The history of the pescatarian diet can be traced back to Classical Greece, where at the time it was essentially synonymous with vegetarianism. In the centuries since then, various cultures and prominent figures have advocated for a meatless diet for a number of different reasons, including the perception that eating fish and vegetables is a fundamentally more healthy option. Health wasn’t always a factor, though; in Japan, for instance, the consumption of meat from livestock was banned and remained absent from the Japanese diet for over 1200 years because of growing Buddhist influences.
In many cultures that developed along coasts or on islands, the population tended toward a pescatarian lifestyle more out of necessity than choice, however. In more recent history, the overlap between pescatarian and vegetarian diets has continued, in large part because of the idea that fish and other types of seafood don’t count as “meat.” These days, the pescatarian diet is closely related to other diets like the flexitarian diet and the Mediterranean diet. The common feature they all share is that they are derived from real-world examples of diet being a key component of an overall healthy lifestyle.
How Does the Pescatarian Diet Work?

The most basic definition of the pescatarian diet is a primarily plant-based diet that incorporates fish and other seafood as a source of animal protein. In fact, many pescatarians may even identify as vegetarians who only occasionally eat fish. While there isn’t a specific pescatarian diet plan or system, there are a few principles and key features that set it apart:
- Plant-based: Ironically, even though by definition pescatarians eat fish, the diet fundamentally revolves around plant-based foods like fruits, veggies, whole grains, legumes (which includes beans and lentils), nuts, seeds, and healthy fats like olive oil.
- Seafood: Unsurprisingly, another key aspect of the pescatarian diet is an emphasis on fish and shellfish as the main protein source. Virtually any type of fish is acceptable, but some popular examples are sardines, swordfish, tilefish, light tuna, and king mackerel. Some pescatarians only eat fish, while others also include shellfish like shrimp, lobster, clams, and scallops.
- No meat: The pescatarian diet also makes a distinction between seafood and other animal proteins derived from livestock animals. This means the diet specifically excludes red meat, poultry, pork, and game meats.
- Dairy products: Dairy products like milk, cheese, and eggs are sometimes a point of dispute amongst pescatarians. Some people regularly include dairy products along with eating fish and plant foods. Other pescatarians lean toward principles associated with a vegan diet and won’t eat meat or any other animal products at all apart from fish.
- Eco-conscious: Traditionally, a pescatarian diet was conceived primarily as a means of improving overall health and wellness. It’s only in the last few decades that pescatarian, vegan, and vegetarian diets have also become known for their alignment with concerns about issues like animal welfare and environmental sustainability. This newer aspect of the diet comes in part from substantial research about the environmental impact of animal agriculture on greenhouse gas emissions and the overuse of water and land resources.
- Flexibility: The pescatarian diet is very similar to (and overlaps with) the flexitarian diet in the sense that it allows adherents a lot of leeway in how it is used. Pescetarianism might even be considered a compromise between meat-eaters and vegetarians as a healthy diet that isn’t too restrictive. At the core, though, is a type of flexibility that allows some pescatarians to eat seafood regularly while others may only do it occasionally.
What Are the Health Benefits of a Pescatarian Diet?
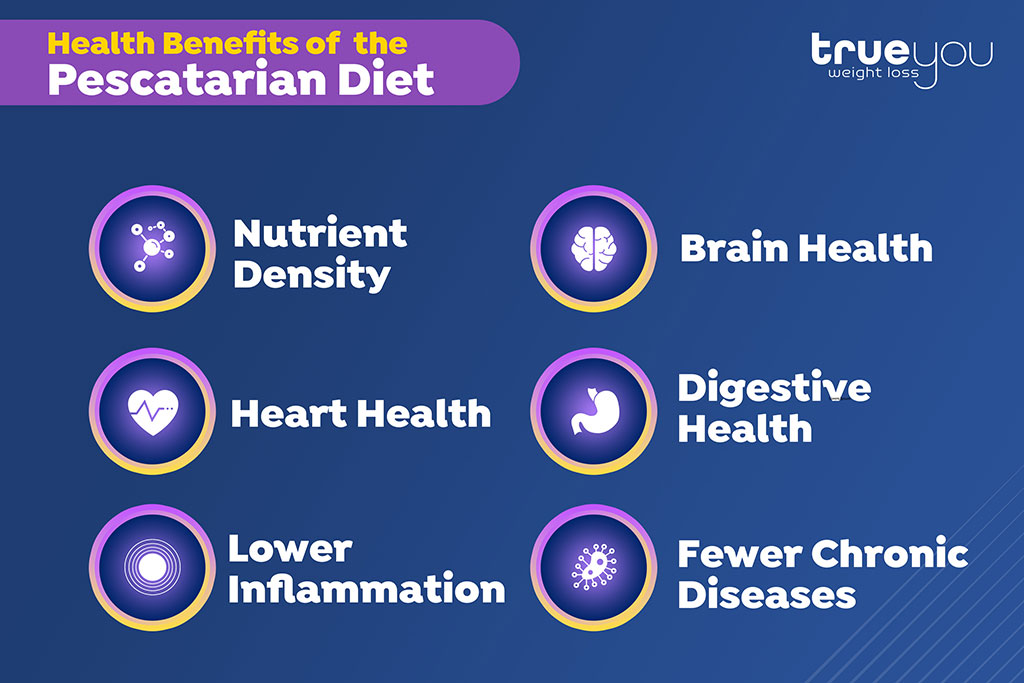

As scientists have continued to research the ways our diet can affect our body, it has become clear that some eating patterns are more healthy than others. The typical American diet, for example, tends to be high in refined carbs, saturated fat, and cholesterol, which are all factors that raise the risk for heart disease, obesity, and other related conditions. The pescatarian diet, on the other hand, emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods and offers similar health benefits as the Mediterranean diet, the DASH diet, and the MIND diet. Below is an overview of these health benefits:
- Nutrient density: As noted, highly processed foods are often high in fat and carbohydrates while being low in protein, fiber, and valuable vitamins and minerals. This kind of diet often means having deficiencies in essential nutrients that the body needs to function. But a diet like the pescatarian diet is rich in minerals like iron and calcium as well as vitamins like vitamin B12 and D.
- Heart health: One of the most important benefits of the pescatarian diet is its impact on the health of the heart and the risk of cardiovascular disease. This is in part due to the high mineral content and how it helps improve the circulatory system and reduce high blood pressure. Fatty fish like salmon and mackerel are also rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which are compounds believed to lower triglyceride levels and improve overall heart health.
- Lower inflammation: Inflammation is part of a normal immune system response, but there are many health problems that are characterized by inflammation getting out of control. The omega-3 fatty acids contained in fish are also believed to reduce inflammation levels and potentially lower the risk of developing an inflammatory condition.
- Brain health: Many of the nutrients and compounds in fish and plant-based foods are also helpful for maintaining brain health and even slowing down age-related cognitive decline.
- Digestive health: The fiber-rich plant foods that are central to the pescatarian diet are also very helpful for bowel motility and overall digestive health. The fiber and nutritional content may also lead to a lower risk of various gastrointestinal disorders.
- Fewer chronic diseases: The foods emphasized in the pescatarian diet are generally higher in antioxidants. Antioxidants are substances that can absorb and protect the body’s cells from free radicals, tiny particles that can damage body tissues by forcing the body into a state of oxidative stress. Oxidative stress is believed to play a significant role in the development of numerous chronic diseases like type 2 diabetes, neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s, or even some types of cancer.
What is the Environmental Impact of the Pescatarian Diet?
One of the other major reasons people advocate for the pescatarian diet is because of its potential lower impact on the environment. Though there are some ways the impact can be negative (overfishing, water contaminants, or habitat damage, for example), there are several aspects of fishery practices that make them better for the environment when compared to animal agriculture:
- Fewer emissions: Fish farming and wild fisheries tend to have a lower carbon footprint compared to land-based animal agriculture because vast herds of livestock release substantial amounts of methane and other greenhouse gasses into the atmosphere.
- Reduced land use: Producing seafood typically requires less land compared to raising livestock for meat production, and this can help reduce deforestation and habitat destruction.
- Less resources used: In general, seafood production requires less energy and other resources to operate; it’s also quicker and easier to process fish to prepare for human consumption.
Can the Pescatarian Diet Lead to Weight Loss?
Like the Mediterranean diet and other meal plans that are primarily concerned with health, the pescatarian diet might not be a person’s first choice for weight loss. Nevertheless, there is evidence that an eating pattern defined by pescetarianism can be helpful for losing weight or maintaining a healthy weight. There haven’t been many studies specifically on whether the pescatarian diet leads to weight loss, but there has been a lot of research that shows how shifting to a diet based around plant-based foods and lean proteins like fish can promote a calorie deficit in some people.
Indeed, fish consumption in the pescatarian diet is one of the main reasons it can be helpful for weight loss. In the typical American diet, red meat and pork are common, but they also are both high in saturated fat and calories. So even though they are good sources of protein (an important macronutrient when trying to lose weight), the amount of fat and cholesterol make them unhealthy to eat on a regular basis. But fish and many other types of seafood are relatively low in calories at the same time as being loaded with protein; they also contain omega-3 fatty acids and other nutrients that make them filling and beneficial for other aspects of health.
In general, a diet that is high in fiber and protein and low in fat and sugar is going to be ideal for weight loss goals. With the pescatarian diet, the lean proteins from fish and plentiful fiber from plant foods makes it well positioned to create a calorie deficit. As with any kind of diet that is being used for weight loss, though, the ability to actually lose weight is entirely dependent on daily food choices. With the right planning and discipline, the pescatarian diet can be a sustainable way to maintain a healthy weight.
What Do the Experts Say?
Kathleen Walton, MS, RD, LDN, a registered dietitian at Eat Healthy Be Healthy, offers some insight into commonly asked questions about the pescatarian diet:
What are the pros and cons of the pescatarian diet? What type of people may benefit from this diet and who should avoid?
- Pros: Many different health benefits. Fish (especially fatty fish like salmon) are high in Omega-3 fatty acids. These fatty acids help keep your heart healthy, lower risk or certain cancers, decrease likelihood of diabetes, and decrease inflammation. In addition, adding fish to a vegetarian diet can increase nutrients such as vitamin B12, zinc, selenium, calcium, and protein.
- Cons: Risk of heavy metals and pollutants from marine fish. Some fish (shark, sword fish, king mackerel, etc) have high levels of mercury.
What have you found people are generally unaware of when considering the pescetarian diet?
- The pescetarian diet is for people who chose to follow a plant-forward diet (omitting red meat and poultry) while still including fish and shellfish. This style of eating is very similar to a vegetarian diet with fish consumed daily or multiple times per week.
- This diet could be helpful for those who want to follow a vegetarian diet but are looking for protein options outside of plant-based options.
Do you have firsthand experience with the pescatarian diet, whether it’s something that you’ve personally tried, or have seen others be successful or unsuccessful with?
- Yes! I have many patients and peers in my personal life who follow a pescetarian diet. Many people have success following the pescetarian diet if they want to follow a vegetarian diet but are looking for occasional seafood options, mainly for additional protein and added vitamins and minerals. This style of eating is also helpful for decreasing inflammation and aiding in health benefits associated with following a plant-forward style of eating.
How much weight do people typically lose with the pescetarian diet?
- If someone has the goal to lose weight, following a plant-forward pescatarian diet (focusing on fruits, vegetables, seafood, whole grains, low-fat dairy, legumes, nuts and seeds), while avoiding heavily processed foods and refined grains can lead to weight loss. The pescatarian diet, itself, is not intended for weight loss but instead intended for additional health benefits and lowering risk of chronic disease.
For someone that might be considering the pescetarian diet what alternative options should they consider and why?
- For people who are interested in the pescetarian diet, the Mediterranean diet might be a great alternative. This style of eating is very similar to the pescatarian diet, with the addition of lean poultry. The Mediterranean diet also has many different health benefits and chronic disease-lowering associations!
Bottom Line
The pescatarian diet, which is essentially a plant-based diet combined with some seafood, is ultimately a heart-healthy and nutrient-rich eating plan. It shares a number of core tenets with other well-regarded diets like DASH, MIND, and the Mediterranean diet. While not specifically intended for weight loss, a pescatarian way of eating can be a useful framework for a weight management plan. The bottom line is that the emphasis on whole, minimally processed, whole foods and lean proteins makes it a great option for some people.
Dieting and Weight Loss
As noted, the pescatarian diet may help some people lose weight, but it will probably only be effective if you enjoy eating seafood. In other words, there isn’t anything magical about the pescatarian diet or any other diet that promotes weight loss. An effective diet plan only works if the person using the plan can realistically follow the diet consistently. But if you’re going to hate the food, there’s a much higher likelihood of abandoning the diet and going back to eating more calories than the body needs.
This dynamic illustrates why weight loss is so hard for most people: because there are numerous factors that lead to weight gain and numerous factors that can be an obstacle to weight loss. In fact, various studies over the years have consistently shown that most (around 80%) people who lose weight through traditional methods like dieting and exercise end up regaining a significant portion of that weight within 12-24 months. This suggests that the specific diet a person selects is less important than sticking with whatever the chosen diet is.
Sustainable Weight Loss with True You
Given the difficulties involved in losing weight, and the demonstrated lack of effectiveness of dieting, it might be tempting to throw your hands up in frustration. But even though many Americans haven’t found their way to sustainable weight loss doesn’t mean it’s actually impossible. Fortunately, advances in endobariatric surgery have provided new weight loss options that weren’t previously available, and there are a lot of people who are eligible for such procedures but who don’t take advantage of it.
At Eat Healthy Be Healthy, we know how challenging a weight loss journey can be. That is why we specialize in the latest non-surgical endobariatric procedures like endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG); with a short, minimally invasive procedure, you can be well on your way to the kind of long-term weight loss that once seemed unimaginable. If you’d like to learn more about ESG or any other alternative weight loss options, please contact us today to request a consultation. Freedom is waiting!
